Multi Perspective Issuance Corroboration (MPIC): Distributed Validation for Securing DNS and CAA Checks
Multi Perspective Issuance Corroboration (MPIC) enhances the security of DNS and CAA validations by conducting checks from multiple geographically distributed locations. This approach mitigates the risk of BGP-based attacks by ensuring that validation results are consistent across regions. SwissPKI supports MPIC with configurable rules, remote perspectives, and regional groupings for secure certificate issuance.
Multi Perspective Issuance Corroboration was introduced by the CA browser forum to counter attacks on the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). Such attacks can be used to attempt to redirect the requests for CAA and Domain Owner checks to one’s own infrastructure and thus pretend to have control over a domain.
MPIC counters such attacks by performing CAA and domain owner checks simultaneously from several geographically different regions. If the results from the regions differ from the result determined by the CA itself, this is an indication of a possible attack and the fact must be taken into account when issuing the certificate.
SwissPKI supports MPIC, whereby the configuration consists of the following three core elements:
-
MPIC Rules – to controll the rules under which MPIC will act.
-
Remote Perspectives – to register and control the remotely deployed remote perspective services.
-
Regions – a means to group the remote pespectives deployed in the same region together and thread them under the same conditions by the MPIC Rules.
With the introduction of Multiple Network Perspectives Corroboration (MPIC) , DNS and CAA validations are executed via several independent remote perspectives.
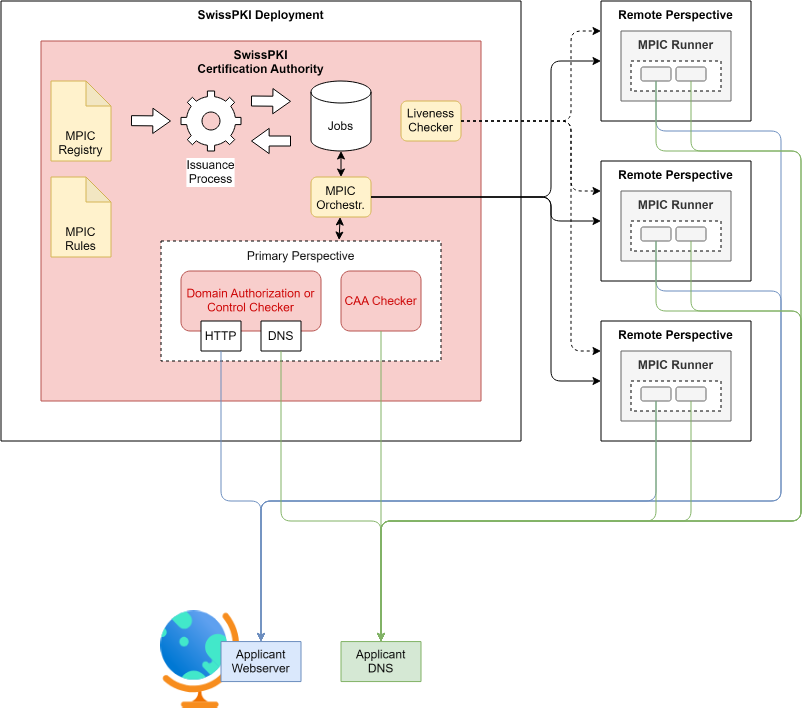
In order to manage and orchestrate this distributed check execution, the Certification Authority process flow relies on the configuration and deployment of the following:
MPIC Registry
Manage the individual remote perspectives for distributed validation requests.
MPIC Rules
Manage rules for the minimum number of remote perspectives, the required quorum and how strictly the results must be taken into account.
MPIC Orchestration
Handles the domain validation or CAA check which remote perspectives such that incoming results are validated to ensure that the necessary quorum is reached. The orchestration takes care of the repeated distribution and validation of results until a check can be considered completed.
Liveness Checker
Verifies the availability and responsiveness of the individual remote perspectives. Failed nodes may no longer be served with check tasks and the system must know whether sufficient nodes are still available. The Liveness Checker verifies at defined intervals that all known nodes are functional. The status of the individual nodes is also reported back to the MPIC Registry so that conformity with the current rules is verified there and alerts triggered if necessary.